For retail brands setting up their offline presence, the cost of setting up a store is enormous. The huge capex and the monthly recurring opex keep piling on every month and with each store opened. When the brands lack a strategic approach to retail expansion, the chances are higher for this cost to negatively impact their overall profitability and growth.
In this article, we navigate the expenses involved with starting a retail store. Whether you’re a seasoned retailer or a novice entrepreneur, understanding the true cost of launching a retail venture is the first step toward sustainable success.
1. Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditure is the initial investment required to start a retail business venture. The capital needed to get placed on the starting line differs across businesses.
For example, the capex of a hypothetical fast-food restaurant business might only be ₹10lakhs, while the cost to start a grocery store would be ₹5lakhs, depending on extraneous factors.
The CAPEX cost of a retail store is an umbrella term for everything from upfront land costs to licenses and technology required to operate the business.
Detailed below are some of the CAPEX costs for a retail store.
i) Buildings or Land
Land is an essential factor when discussing retail. The second factor is its location; after all, the location of the land is the determining factor in the success of a retail store.
The commercial rental rate of a location is determined by multiple factors, including the presence of a vibrant retail market and paying customers.
You wouldn’t expect to pay high-street prices for a location in the middle of nowhere now, would you?
The price of real estate can vary significantly within the same city, depending on the factors above.
Utilizing a location intelligence platform like GeoIQ can help make better decisions knowing the average commercial rent, footfall data, demographics data, etc. across India.

ii) Retail Payment Technology
Technology brings transparency to retail transactions and helps the retail merchant predict future sales trends.
Integrating point-of-sale systems helps improve a business’s revenue and is essential to any modern retail store.
Point of Sale System
The Point of Sale machine is now present in most retail stores in India. The POS system is a comprehensive technology solution that helps retail businesses track their sales, inventory, and customer interactions.
There are four significant types of POS systems classified based on their usage.
Legacy (in-store systems): Consider these systems the grandfather of the current POS machines. They operate in a closed internal network with the collected data stored within the premises. The problem with these POS systems is that managers must be present in person to analyze reports.
Cloud-based systems: Most POS systems used in retail stores today are cloud-based. A step up from the legacy system, they leverage cloud-based applications’ computational power to analyze real-time reports. Furthermore, these systems enable managers to view reports remotely and are cheaper than traditional variants.
Mobile systems: You would have noticed these systems at a small-scale retail store near you or an art fair. They have a single card reader that can be mounted onto the charging port of a mobile device. It is best suited for mobile businesses that do not need dedicated storage for their products.
Self-Service system: The last time you went to a McDonald’s, you would have noticed a self-service kiosk at the store’s entrance. You can select your desired food and pay your charges through the touchscreen. This evolution of the POS system removes the human element from the transaction process, reducing the customer’s waiting period and allowing your employees to focus on other activities.
So, how much will setting up a tech stack cost you when opening a retail store?
Internationally, the price of a POS system ranges between $700 and $1,500, with an additional $500/month for the software needed to run the machine. A merchant can integrate a payment gateway and negotiate a more favorable fee.
iii) Licenses and Insurance
We live in a society, and every business that functions within the society abides by the rules and regulations governing it.
Before an entrepreneur can start a retail business, they need to apply for a few licenses from the government to ensure seamless operation by following established regulations.
Trade license: Issued by the municipal body where the business is present. The trade license grants permission to the retail store to conduct business in the locality. The fee of the license varies depending on the state. From ₹25 in Karnataka to over ₹5,000 in Telangana, a trade license is the first item on the checklist of a budding entrepreneur.
Shops Act: To protect the interests of employees in a business establishment, the labor department of each state in India administers the Shops and Establishments Act. Every retail store that starts a business requires this authorization from the government before it can start operation. The registration fees to get a shop license vary from state to state. In Karnataka, for example, a prospective retail entrepreneur will pay between ₹300 and ₹75,000 depending on the number of employees.
FSSAI Certificate: A mandatory certificate that every retail brand selling food or perishable items needs to acquire before starting their business. The license regulates the standards for food-based products in India. Retail entrepreneurs can get an FSSAI certificate by paying a registration fee of ₹7,500.
Retail Insurance: A forward-thinking retail entrepreneur should also invest in insurance covers for their retail business. From insuring a business against losses accrued due to fire damage to liability insurance, the various insurance policies available in the market account for this and many other business risks. Basic Commercial General Liability insurance for businesses in India has a small premium generally between ₹5,000 and ₹20,000 annually.
iv) Renovation Cost
Retail stores seldom come gift-wrapped in the perfect dimensions suiting the retail category. One of the first tasks a new retail store entrepreneur should commit to is renovating their store.
For example, you would want to open a mobile phone store, and the store you purchased would have been outfitted for a small grocery store. You must remove the existing infrastructure and install a new interior framework that suits a mobile phone store.
When considering options for renovation, the retailer should consider the prevailing market rates for labor. In a major city like Bangalore, that is between ₹280/sq ft to ₹320/sq ft and can vary depending on the negotiating capability of the retailer.
2. Operating Expenses
The expenditure resulting from the day-to-day functions of a retail business.
The OPEX cost of a retail store is one of the few factors in retail that can be predicted with a degree of certainty. Given below are a few of the various factors that contribute to the OPEX bill of a retail store
I) Salary or Wages
The component of any business operation keeps the cogs’ wheels turning. Salary constitutes 10% to 20% of the total revenue in a retail business operation.
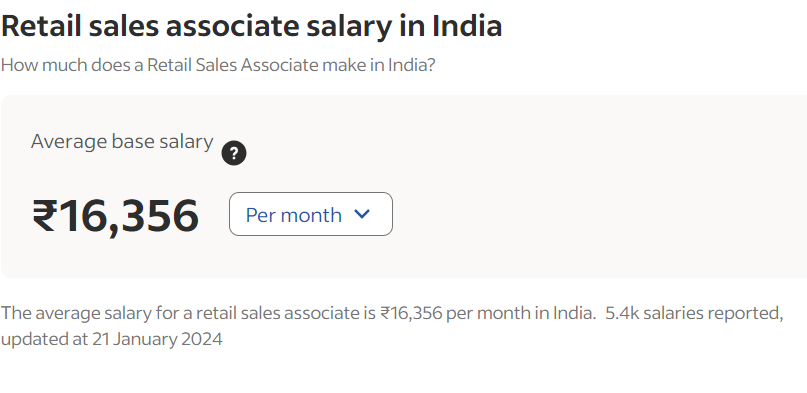
This average salary for a retail sales associate from Indeed identifies a median of ₹2.31 LPA or a monthly salary of ₹16,356.
For example, consider a hypothetical scenario where a retail store employs five people. To ensure that salary constitutes at least 10% of the revenue, the business would need to generate monthly of at least ₹7,00,000.
ii) Marketing
Once a store is up and running comes the hard part.
Getting customers through the doors and buying your products. And there lies the importance of marketing in retail.
This Gartner report pegs the average marketing budget for a retail store at 9.5% of the total revenue. For example, if your store has a revenue of ₹1lakh per month, you should only spend ₹9,500 on your marketing budget.
One of the easiest ways to get in front of your target customers is to print flyers and deliver them within a target location. Businesses could choose to,
- Insert their pamphlets into the morning newspaper of customers in their trade area.
- They could task a delivery company.
According to this service provider, a newspaper insert can cost ₹0.55/pamphlet with an impression of 1.4M in Bangalore city.
Retail businesses should also invest in local SEO, email marketing, and other local marketing activities. Fine-tuning local SEO helps local businesses stand out from the competition. Given the result from GE Retail Bank’s study, which identified that 81% of all customers search online before buying a product, a retail business must have an online presence.
iii) Inventory
Picture a retail store that does not have any products to sell. You can draw two inferences from this image: either there is a stockout, or the store is going out of business/already out of business.
The success of a retail store depends on its ability to restock its inventory accurately. Let’s understand how a business can bleed money through incorrect inventory expenditure.
There are four costs associated with inventory,
- Purchase cost: The cost of purchasing a product from the manufacturer or wholesaler.
- Transportation cost: The cost of getting the product from the wholesaler to the retail store. This will include the price of transportation and labor charges.
- Storage cost: Costs associated with storing a retail product. For example, in the case of perishable goods like milk or vegetables, they require refrigeration, or they will decay, leading to spoilage. And in some cases, retailers may have to rent large warehouses to store their perishables.
- Cost of lost opportunities: Retail inventory management fails when retailers fail to manage their sales cycle adequately.
For example, imagine you are selling in-season fruits from a kiosk, and you run out of the product owing to expected demand. But you did not factor in this increase in sales, so you do not have anything to sell.
- You now lose the customer who still needs to get the product.
- You incur losses when you try to meet the market demand by rushing to fill inventory and paying a premium for transportation.
Employing a forecasting method will enable the retail store to reduce the costs associated with getting overstocked. And for the other expenditures, the retailer can negotiate with the primary businesses to strike an amicable deal.
Conclusion
To recap,
These are some of the costs associated with starting a retail store in India
Capex Cost
- Land cost or rent
- Retail payment technology
- Licenses and Insurance
Opex Cost
- Salary or Wages
- Gateway payment/Card payments
- Marketing
- Inventory
While not exhaustive, these factors contribute to a sizeable portion of the cost involved with starting a retail store in India. The cost associated with land/rent of the property occupies a large part of any retail business outlay. It is also one of the factors that most retail entrepreneurs predict incorrectly.
An entrepreneur presented with only some of the data can draw incorrect conclusions resulting in huge capex losses. A retail entrepreneur might also be led astray due to the prevailing market sentiments. For example, a retail broker might convince an entrepreneur that a location will yield multiple returns on the investment. However, the broker might not understand why the specified location is working for a particular category of retail business.
Now, what if the entrepreneur had access to a revolutionary location analytics AI solution that is custom-built for the business?
Presenting RetailIQ
RetailIQ is a cutting-edge AI solution revolutionizing offline expansion for the retail section. It is built on top of extensive location data and brands’ data to give street-level answers to expansion problems.
RetailIQ is a powerful tool providing site recommendations to maximize success at the store level and minimize the risk of closure. It also helps in identifying the total addressable market, competition analysis, a better understanding of your target audience traits and their presence, detailed site analysis, and reports, all adding up to a successful expansion strategy.


