In India, retail has been one of the fastest-growing industries, with its market capitalization reaching $1.2 trillion in 2023.
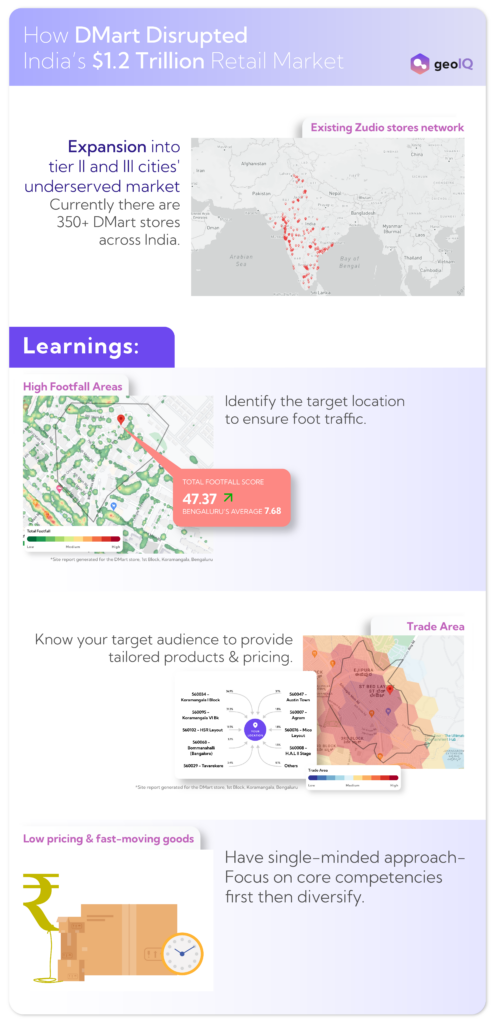
Among the various players in this competitive industry, DMart has successfully marked itself as a market leader with its 350+ stores across 13 states as of 2024.
This article examines DMart’s successful journey, starting from its inception, and the unique business model that has driven its success.
How DMart Was Founded?
Before venturing into retail, Radhakishan Damani was well-known in the Indian stock market for his long-term investment strategies. However, he saw an opportunity in India’s organized retail sector, which was still in its early stages in the early 2000s.
In 2002, Damani opened the first DMart store in Powai, Mumbai, with a simple mission: to provide Indian consumers with high-quality goods at affordable prices.
His goal was to cater to the needs of middle-class families, offering products ranging from groceries and kitchenware to personal care items and clothing- all under one roof.
His understanding of consumer behavior and rapid scaling throughout the states laid the foundation for DMart’s long-term success.

Source: GeoIQ
DMart’s Business Model and Strategy: Factors that Contributed to DMart’s Success Story
DMart’s business model is an amalgamation of multiple retail strategies and here’s a detailed breakdown of the strategies that underpin DMart’s success:
1. Everyday Low Pricing (EDLP)
The core of DMart’s retail business model is its “Everyday Low Pricing” strategy. Unlike other retailers where they’d run discounts based on seasons and other reasons, DMart offered consistent offers throughout the year. This appealed to the masses, especially for the middle-class consumers.
To ensure profit and to make the price relatively lower than the competitors, DMart saved costs through bulk purchases directly from manufacturers, rather than involving any intermediaries.
Moreover, this EDLP strategy not only attracts footfall but also encourages repeat customers, fostering long-term loyalty.
2. Cautious Expansion Strategy
While many retailers focus on rapid expansion to gain market share, DMart has adopted a slow and steady approach:
Market Research: Each new store location is chosen after meticulous analysis of factors such as residential density, purchasing power, competition, etc.
Profitability First: DMart ensures that every new store is profitable within a short period, avoiding the financial strain of underperforming locations.
DMart took the slow and steady approach majorly because of the fact that DMart had faced complexities in choosing the right location for their new stores.
GeoIQ’s location intelligence platform can ease off this burden by providing multiple, crucial location datasets such as footfall, customer demographics, customer density, competition, etc to find a perfect location.
Utilizing such a platform can help pick the right location with over 95% accuracy while expanding rapidly!

3. Owning Store Properties
One of DMart’s standout strategies is its preference for owning its stores rather than leasing them. This decision, while capital-intensive initially, offers two major long-term benefits:
Cost Savings: By avoiding rent expenses, DMart minimizes operating costs.
Control Over Operations: Ownership allows DMart to customize its store layouts and ensure operational efficiency without external constraints.
4. Focus on High-Demand, Fast-Moving Products
DMart’s product selection is highly curated, focusing on essential and fast-moving goods such as groceries, FMCG products, and household items.
This ensures that the products are sold quickly, reducing the risk of unsold inventory.
Similarly, for any retail business, identifying the best selling products for their store at a particular location should be decided using location data. In fact, one of our clients utilized location data to optimize their merchandising strategy which resulted in 45% more sales!
5. Efficient Supply Chain
DMart’s supply chain is a well-planned one that minimizes costs and maximizes efficiency.
Bulk Purchasing: As we mentioned earlier, DMart purchases products in bulk directly from manufacturers, eliminating intermediaries and securing better prices.
Efficient Distribution: A streamlined logistics network ensures products are transported swiftly from manufacturers to stores, reducing delays and lowering transportation costs.
Vendor Relationships: DMart maintains strong relationships with its suppliers, negotiating favorable terms and ensuring a steady flow of goods.
6. Lean Operational Model
DMart operates with a lean organizational structure, minimizing overhead costs. For instance, the company spends very little on advertising, relying instead on word-of-mouth and in-store promotions to attract customers.
The Numbers Behind DMart’s Success
DMart’s impact on India’s retail market is evident from its impressive financial performance:
Revenue: DMart reported a revenue of $547.24 Billion, growing steadily year-on-year
Market Share: It holds a significant share of the organized retail market, outperforming competitors like Big Bazaar and Reliance Retail.
Profitability: Unlike many major retail chains that faced underperformance and store closure, DMart performed well and consistently delivered strong profit margins.
Lessons From DMart’s Success Story
1. Know Your Location
Location is critical for any retail business. DMart carefully selects store locations based on population density, and potential demand, often targeting suburban and semi-urban areas with growing middle-class populations. This ensures consistent foot traffic and long-term viability.

2. Understand Your Customers
DMart’s deep understanding of its target audience – primarily middle-class families – allows it to tailor its product range and pricing to meet their needs.
3. Focus on Core Competencies
Rather than diversifying into unrelated ventures, DMart focuses on what it does best: providing affordable essentials. This single-minded approach has allowed DMart to optimize operations and maintain cost leadership in the market.
Conclusion
DMart’s success story is solid proof that a well-defined, data-backed, and, most importantly, customer-focused retail business can succeed even in a fiercely competitive market like retail in India.
If you are an entrepreneur or retailer looking to scale your business, make sure you understand your target customers and location better with location intelligence to remove any bottlenecks.



Pingback: Value Retail at Its Best: Why DMart’s Everyday-Low-Price Strategy Still Works for Indian Consumers